Fiveable AP World Unit 6 embarks on an extraordinary journey through a pivotal period in world history, unveiling the complexities of global change and its profound impact on societies and civilizations. From political upheavals to cultural advancements, this unit promises an immersive exploration of the forces that shaped our world.
As we delve into Unit 6, we will uncover the historical context that set the stage for transformative events, examine major themes and concepts that shaped world history, and analyze the roles of key figures and groups who played a pivotal role in shaping its course.
Historical Context of Unit 6
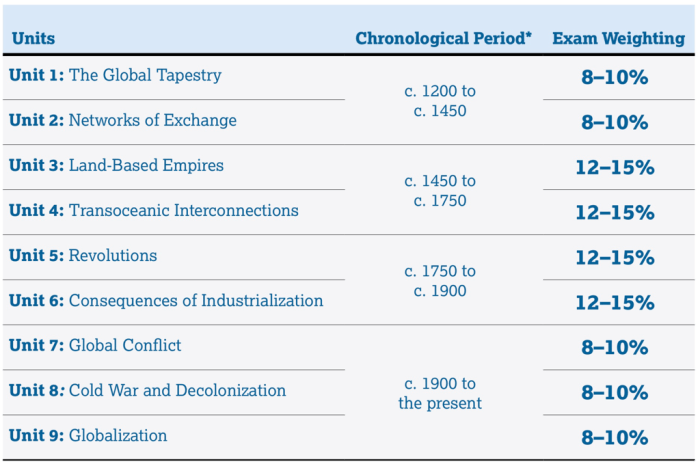
Unit 6 covers a pivotal period in world history, spanning the 18th century to the early 20th century. This era witnessed profound transformations that laid the groundwork for the modern world we know today.
Key events and developments during this period include:
- The Enlightenment, which emphasized reason, individualism, and scientific inquiry.
- The American and French Revolutions, which challenged traditional monarchies and established democratic ideals.
- The Industrial Revolution, which introduced new technologies and transformed economic and social structures.
- The rise of nationalism and imperialism, which shaped global politics and led to increased competition and conflict.
- The emergence of new global powers, such as the United States and Germany, which challenged the dominance of European empires.
Major Themes and Concepts
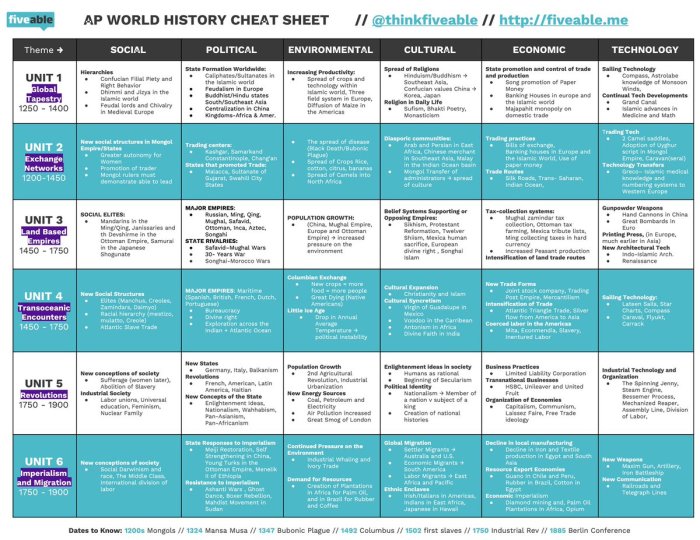
Unit 6 of AP World History explores several central themes and concepts that have shaped the course of human civilization.
One key theme is the rise and fall of empires. Throughout history, powerful empires have emerged, dominating vast territories and influencing the development of civilizations. However, these empires have also experienced decline and collapse, often due to factors such as internal strife, external pressures, or technological advancements.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations have played a crucial role in shaping world history. From the invention of the wheel to the development of gunpowder and the printing press, technological advancements have transformed societies, facilitated communication and trade, and altered the balance of power.
Cultural Exchange and Diffusion
Cultural exchange and diffusion have also been major forces in shaping world history. As civilizations interacted with each other, they exchanged ideas, beliefs, and technologies, leading to the development of new cultures and the spread of knowledge and innovation.
Environmental Interactions
Environmental interactions have significantly influenced the development of human societies. Climate change, natural disasters, and the availability of resources have shaped human settlements, migrations, and economic activities.
Social and Political Change, Fiveable ap world unit 6
Social and political change have been ongoing processes throughout history. Revolutions, reforms, and the rise of new ideologies have challenged established orders and led to the transformation of societies.
Key Figures and Events
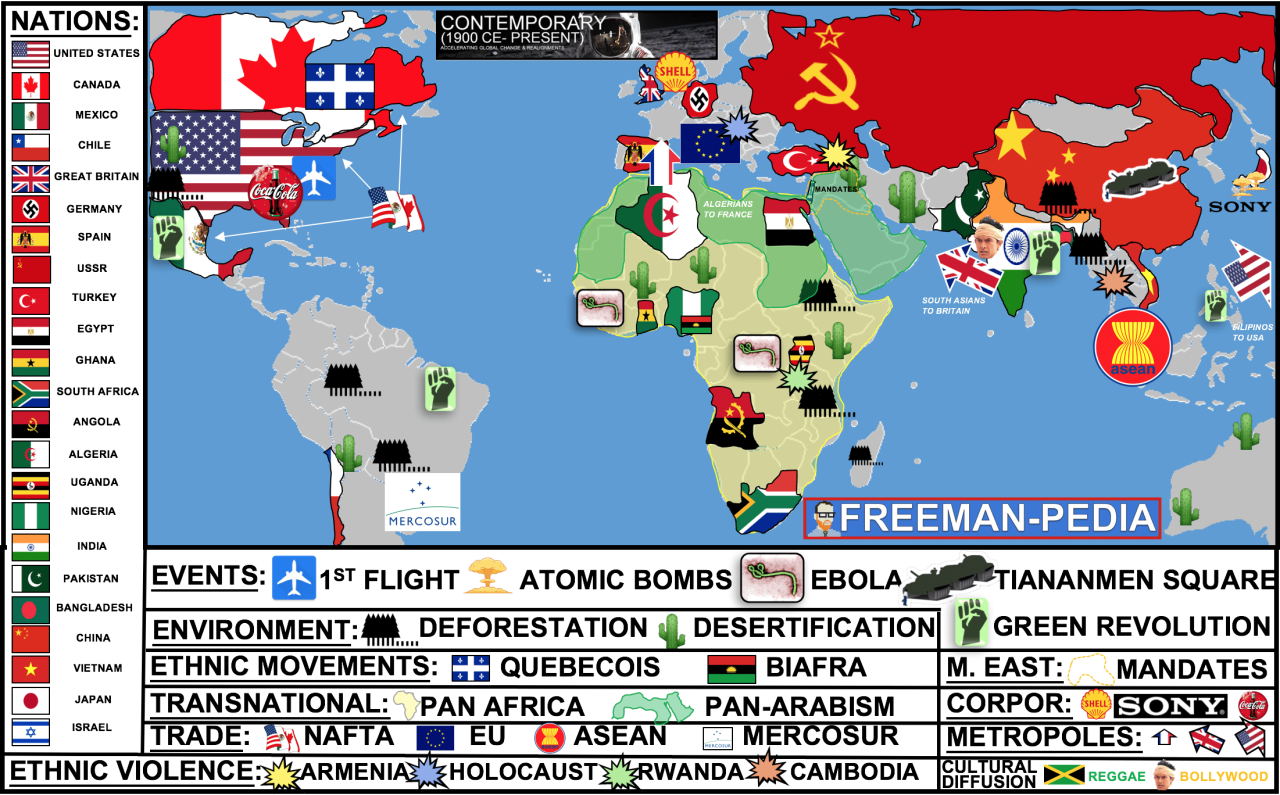
Individuals and groups played pivotal roles in shaping the events of Unit 6, leaving an enduring mark on the course of world history. Events of profound significance served as catalysts for change, reshaping global dynamics.
Key figures such as Otto von Bismarck, Theodore Roosevelt, and Woodrow Wilson emerged as influential leaders during this era, their policies and decisions having a profound impact on international relations and global affairs.
Impact of Imperialism
The scramble for colonies intensified during this period, with European powers competing for control of vast territories in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. This scramble for colonies had far-reaching consequences, including the exploitation of resources, the displacement of indigenous populations, and the redrawing of political boundaries.
- The Berlin Conference of 1884-1885 divided Africa among European powers, setting the stage for future conflicts.
- The Boer Wars in South Africa (1899-1902) exemplified the tensions between European colonizers and indigenous populations.
World War I
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914 sparked a chain of events that culminated in the outbreak of World War I. This devastating conflict, which lasted from 1914 to 1918, reshaped the political landscape of Europe and had a profound impact on global affairs.
- The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, imposed harsh reparations on Germany, contributing to the rise of Naziism.
- The Russian Revolution of 1917 led to the establishment of the Soviet Union, which became a major player in international relations.
Rise of Totalitarianism
In the aftermath of World War I, totalitarian regimes emerged in various parts of the world. These regimes, characterized by their suppression of dissent and their glorification of the state, had a profound impact on the course of history.
- The rise of Fascism in Italy under Benito Mussolini and Nazism in Germany under Adolf Hitler led to the outbreak of World War II.
- The Soviet Union under Joseph Stalin became a totalitarian state, suppressing political opposition and collectivizing agriculture.
Causes and Consequences of Global Change
The sixth unit of AP World History explores the period from 1750 to 1900, a time of profound global transformations. These changes were driven by a complex interplay of factors, including the Industrial Revolution, European colonialism, and the rise of nationalism.
The consequences of these global changes were far-reaching and long-lasting. They shaped the political, economic, and social landscapes of the world, and continue to influence our lives today.
Factors Contributing to Global Change
Several factors contributed to the global transformations of the 18th and 19th centuries. These included:
- The Industrial Revolution:The development of new technologies and the rise of industrial capitalism led to a surge in production and economic growth.
- European Colonialism:European powers established colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, which gave them access to new resources and markets.
- The Rise of Nationalism:The growth of national consciousness and the desire for self-determination led to the formation of new nation-states.
Consequences of Global Change
The global changes of the 18th and 19th centuries had a profound impact on societies and civilizations around the world. These consequences included:
- Economic Inequality:The Industrial Revolution led to the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few, while many workers faced poverty and exploitation.
- Social Upheaval:The Industrial Revolution also led to the breakdown of traditional social structures and the rise of new social classes.
- Political Instability:The rise of nationalism and the decline of empires led to political instability and conflict.
- Environmental Degradation:The Industrial Revolution and the expansion of colonialism led to environmental degradation and the depletion of natural resources.
Cultural and Intellectual Developments
Unit 6 witnessed significant cultural and intellectual advancements that transformed societies worldwide. These developments influenced art, literature, and philosophy, shaping the intellectual landscape of the era.
Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution introduced a new approach to understanding the natural world, emphasizing observation, experimentation, and reason. It led to groundbreaking discoveries in physics, astronomy, and biology, challenging traditional beliefs and expanding human knowledge.
Enlightenment
The Enlightenment emphasized the power of human reason and the importance of individual rights and liberties. It promoted ideas of progress, equality, and the separation of church and state, shaping political and social thought in Europe and beyond.
Arts and Literature
Cultural developments influenced art and literature, leading to the emergence of new styles and themes. Baroque and Rococo art celebrated grandeur and opulence, while Neoclassicism emphasized rationality and order. Literature explored themes of reason, emotion, and the human condition, with works like “Candide” and “Gulliver’s Travels” satirizing society and human nature.
Philosophy
Philosophical ideas flourished during this period. Rationalism, associated with Descartes and Spinoza, emphasized the power of reason to understand the world. Empiricism, championed by Locke and Hume, stressed the importance of experience and observation. These ideas shaped philosophical debates and influenced political and social thought.
Technological Innovations and Economic Changes
The 18th century witnessed remarkable technological advancements and economic transformations that profoundly shaped daily life, trade, and power dynamics globally. These innovations and changes laid the foundation for the Industrial Revolution and had far-reaching consequences for societies and economies.
One of the most significant technological innovations of this period was the steam engine, invented by Thomas Savery in 1698. The steam engine found widespread application in various industries, including mining, manufacturing, and transportation. It enabled the mechanization of production processes, leading to increased efficiency and output.
Another important technological development was the invention of the cotton gin by Eli Whitney in 1793. The cotton gin revolutionized the textile industry by automating the removal of seeds from cotton fibers. This greatly increased the productivity of cotton cultivation and led to a boom in the cotton trade.
The economic changes of the 18th century were closely linked to these technological innovations. The increased efficiency of production led to a decline in the cost of goods, making them more accessible to a wider population. This stimulated consumer demand and fueled economic growth.
Moreover, the expansion of trade and commerce during this period created new markets and opportunities for businesses. The establishment of global trade routes, such as the Triangular Trade, facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between different regions of the world.
The technological innovations and economic changes of Unit 6 had a profound impact on power dynamics. Countries with access to advanced technologies and strong economies gained a competitive advantage in international affairs. This led to the rise of industrial powers such as Great Britain and the United States.
Political and Diplomatic Developments
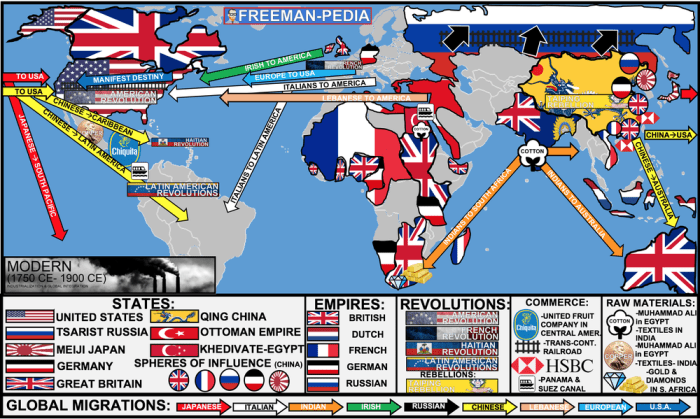
Unit 6 witnessed significant political and diplomatic shifts, marked by the rise and fall of empires, the formation and dissolution of alliances, and numerous conflicts that shaped the global landscape.
The European powers continued to expand their empires, competing for control of territories in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. The British Empire, in particular, reached its peak during this period, becoming the dominant global power.
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, once a formidable power in the Middle East and Eastern Europe, began to decline in the 19th century. Internal political instability, economic challenges, and pressure from European powers led to its gradual disintegration.
- Internal strife and ethnic tensions weakened the empire from within.
- European powers, such as Russia and Austria-Hungary, took advantage of the empire’s weakness and annexed territories.
- The Ottoman Empire’s inability to modernize its military and economy further contributed to its decline.
The Crimean War
The Crimean War (1853-1856) was a major conflict between Russia and an alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, Britain, and Sardinia. The war was fought primarily in the Crimean Peninsula and resulted in a victory for the allies.
- The war exposed the weakness of the Russian military and led to a shift in the balance of power in Europe.
- It also highlighted the importance of international cooperation and alliances in shaping global events.
The Concert of Europe
The Concert of Europe was a series of diplomatic conferences held between 1815 and 1823. The conferences aimed to maintain the balance of power in Europe after the Napoleonic Wars.
For those tackling Fiveable AP World Unit 6, remember to keep your knowledge sharp. If you’re looking for a comprehensive review, check out the ACLS Exam Version A 2023 . This resource provides valuable insights and practice questions that will boost your understanding of Unit 6 concepts.
Continue your prep and conquer the upcoming assessment with confidence!
- The Concert of Europe was based on the principle of collective security, where all powers agreed to intervene if any one power threatened the peace.
- The Concert of Europe was largely successful in preventing major conflicts in Europe for several decades.
Social and Cultural Transformations: Fiveable Ap World Unit 6
Unit 6 witnessed significant social and cultural transformations that reshaped societies around the world. These changes encompassed family structures, gender roles, and religious practices, leaving a lasting impact on the development of human civilization.
Changes in Family Structures
The traditional patriarchal family structure underwent significant changes during this period. In many regions, extended families began to give way to nuclear families, as people migrated to urban areas and sought greater independence. This shift had implications for family dynamics, as women gained more autonomy and decision-making power within the household.
Evolving Gender Roles
Gender roles also underwent a gradual evolution during Unit 6. While women traditionally held subordinate positions in society, they began to challenge these norms and demand greater equality. This movement, known as feminism, led to increased educational and employment opportunities for women, as well as a growing awareness of women’s rights.
Religious Transformations
Religious practices and beliefs also experienced significant transformations. The spread of Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism led to the decline of traditional polytheistic religions in many regions. This had a profound impact on people’s worldviews and social structures, as new religious ideologies provided different frameworks for understanding the world and one’s place within it.
Environmental and Demographic Changes
The period covered in Unit 6 witnessed significant environmental and demographic shifts that profoundly impacted human populations and the natural world. These changes shaped the course of history and continue to resonate today.
One of the most notable environmental changes was the Little Ice Age, a period of cooling that occurred between the 14th and 19th centuries. This cooling led to widespread famine and disease, contributing to population decline and social unrest.
Demographic Changes
The Little Ice Age also had a significant impact on demographic patterns. Population growth slowed, and in some regions, populations actually declined. This was due to a combination of factors, including increased mortality rates, lower birth rates, and increased migration.
Another significant demographic change during this period was the rise of urban centers. As trade and commerce increased, cities grew in size and importance. This led to new challenges, such as overcrowding, pollution, and disease.
Environmental Impacts
The environmental changes of Unit 6 also had a profound impact on the natural world. The Little Ice Age led to the expansion of glaciers and the formation of new lakes and rivers. This changed the landscape and affected the distribution of plant and animal life.
In addition, the rise of urban centers led to increased deforestation and pollution. This had a negative impact on air and water quality, and contributed to the spread of disease.
Conclusion
The environmental and demographic changes of Unit 6 were significant and far-reaching. They shaped the course of history and continue to have an impact on the world today.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of Fiveable AP World Unit 6?
Fiveable AP World Unit 6 covers a crucial period in world history, focusing on global transformations and their impact on societies and civilizations.
What are the major themes explored in Unit 6?
Unit 6 explores themes such as the causes and consequences of global change, the rise and fall of empires, cultural and intellectual developments, and the impact of technological innovations.
How does Fiveable AP World approach the study of Unit 6?
Fiveable AP World provides engaging and accessible content, utilizing videos, interactive simulations, and practice questions to enhance understanding and retention.